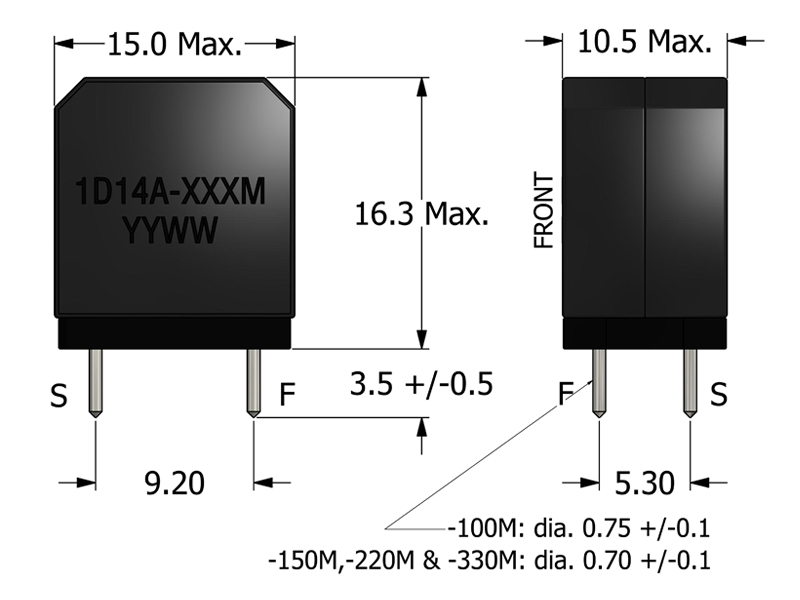
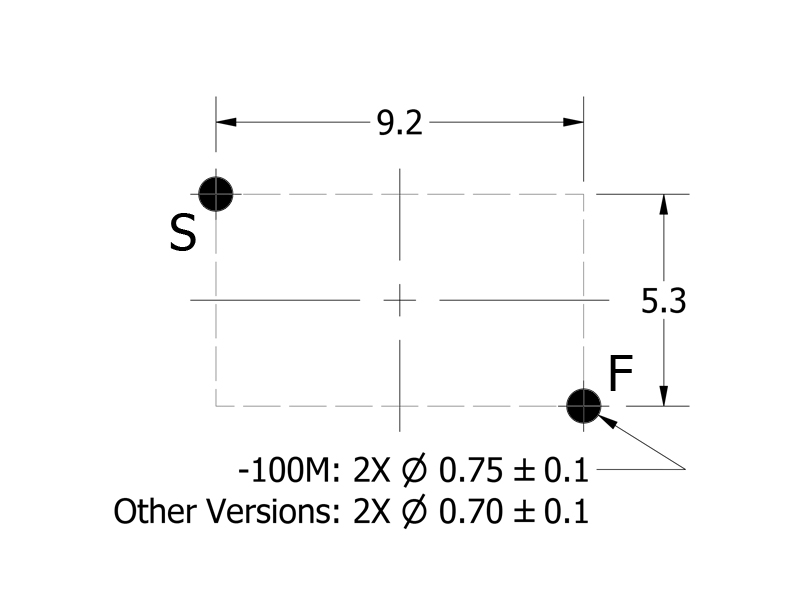
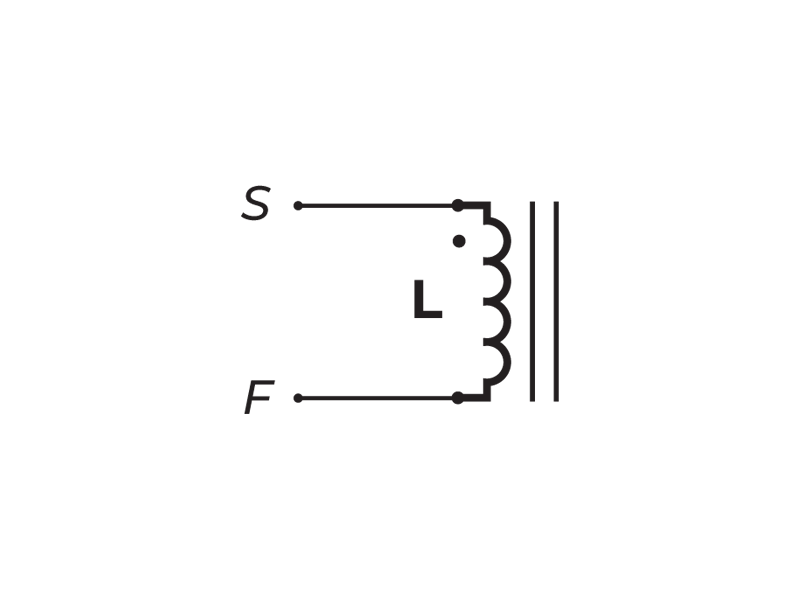-
Operating Temperature Range: The combination of ambient temperature and temperature rise.
-
Inductance: Tested at 1kHz, 1 VRMS, Series.
-
ISAT: DC current through the winding to cause a 10% (typ) drop in inductance.
-
IDC: DC current through the winding to cause a 40°C (typ) temperature rise at 25°C ambient.
-
Flammability Standard: Meets UL 94V-0.
-
SRF: Values are for reference only.
-
Packaging
- Pieces/Tray: 120
- Trays/Box: 9
- Pieces/Box: 1080
-
Specifications subject to change without prior notice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What inductance values and tolerances does 1D14A offer?
1D14A comes in 10 µH, 15 µH, 22 µH, and 33 µH variants (±20%). Higher values increase output-filter effectiveness and lower output ripple; lower values yield faster transient response and lower impedance.
How does shielding benefit 1D14A in audio or sensitive designs?
The shielded ferrite core reduces stray flux and EMI — which helps maintain signal integrity in audio paths and prevents interference with digital circuits or other analog components.
What is the significance of the SRF range (~13.5–24.2 MHz)?
The reference SRF range defines the upper frequency boundary where the inductor behaves inductively. Since 1D14A’s SRF is well above audio and low-frequency switching rates, it ensures stable inductive behavior, minimal parasitic effects, and predictable filtering.
What are the current and saturation limits of 1D14A?
Depending on the variant, saturation current (Iₛₐₜ) is listed up to ~11 A DC. Continuous current causing a 40 °C temperature rise (I_DC) is lower (e.g. ~7.5 A for 10 µH). This fits typical audio amp outputs and low-power supply rails, but not high-current DC/DC rails.
Is 1D14A suitable for high-frequency switching converters?
Not ideal — the series is optimized for low-frequency and audio-rate operation. Though SRF is in the MHz range, the high inductance and ferrite core make it better suited for output filters, not MHz switching power rails.
What design considerations should be made when using 1D14A in audio amplifiers?
Ensure the inductor’s current rating exceeds peak output current, allow margin for tolerance, and layout carefully to minimize loop area — this maximizes filtering efficiency and minimizes EMI or magnetic interference.
How does low DCR contribute to performance?
Low winding resistance reduces I²R losses and heat, preserving efficiency and ensuring clean output — particularly important in continuous audio or DC power circuits.
When is through-hole mounting advantageous over SMT?
Through-hole offers strong mechanical anchoring — ideal for heavier inductors or devices exposed to vibration, handling, or mechanical stress, such as audio amps, power modules, or test boards.
What are typical use cases for 1D14A outside audio?
Low-current DC supplies, small embedded systems, industrial or telecom modules requiring low EMI, envelope-modulated or analog circuits, and any design needing stable, shielded, low-frequency inductance.
What trade-offs come with 1D14A compared to high-current or SMT inductors?
Higher size and inductance lead to lower saturation current and slower transient response. It’s not ideal for high-current, high-frequency switching rails — but excels in audio, EMI-sensitive and low-frequency filtering roles.