-
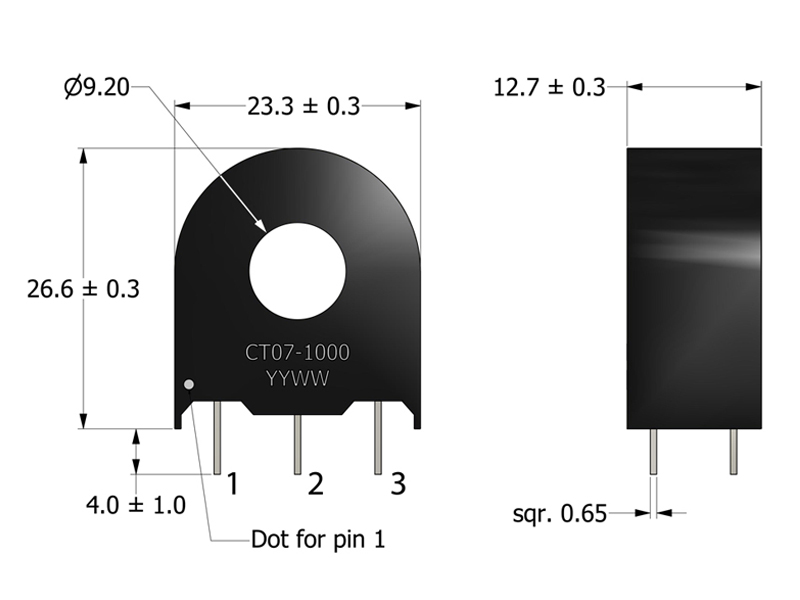
Operating Temp. Range: The combination of ambient temperature and temperature rise.
-
Current Rating: The primary current rating is for reference only and is limited by the current capacity of the customer-supplied primary conductor.
-
Self-Resonant Frequency: The value is for reference only.
-
Flammability Standard: Meets UL 94V-0.
-
Material Rating: Meets requirements for UL Class A temperature rating. Ambient + Temp. Rise + Hotspot Allowance < 105 ºC
-
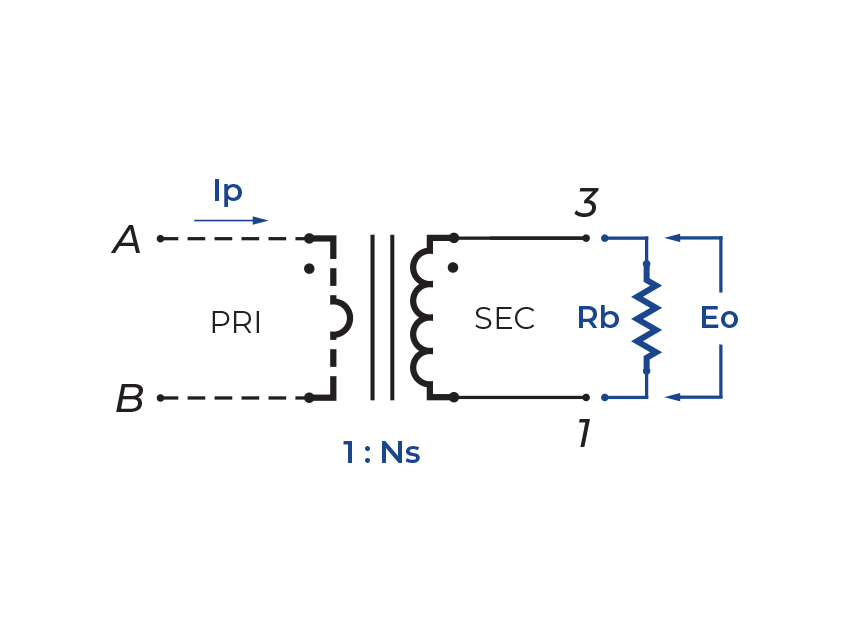
Terminating Resistor (RB): To calculate the value use the formula,
RB = EOTR/IP -
ET Product: Rated at 100ºC. Suitable for bipolar applications only.
ET = EO/2f
EO = IPRB/TR
Whereas,
EO = Output voltage (V) TR = Turns Ratio
RB = Term. Resistor (Ω) f = Frequency (Hz)
IP = Primary Current (A) -
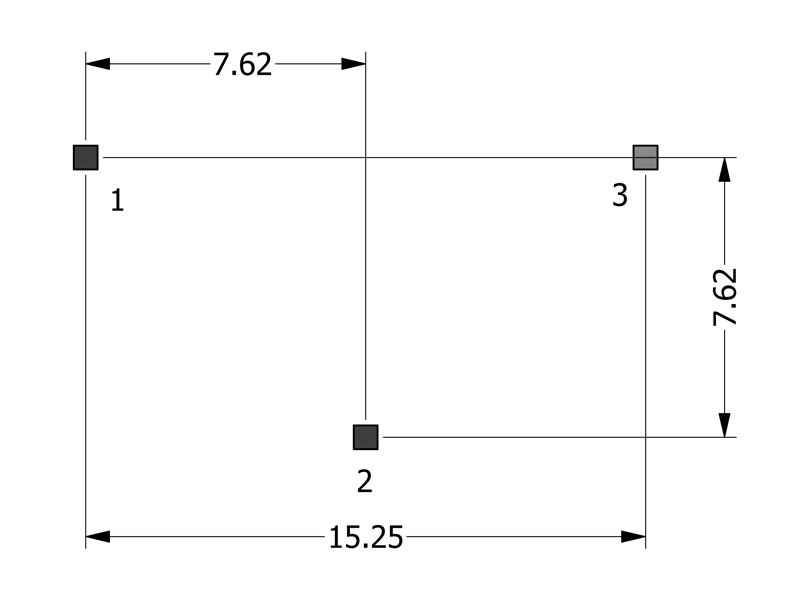
PACKAGING
-
Pieces/Tray: 60
-
Trays/Box: 9
-
Pieces/Box: 540
-
-
Specifications subject to change without prior notice.
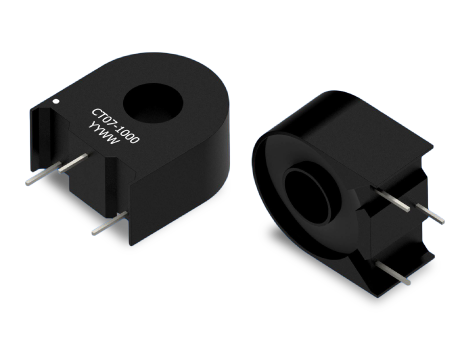
CT07 is designed for high-current AC and pulsed DC measurement, with a reference capability up to 200 A RMS using a single-turn primary conductor. The transformer does not limit the primary current; instead, the actual current rating depends on the gauge and thermal rating of the conductor passed through the core.
The CT07 operates effectively from about 30 Hz to several kilohertz, making it well suited for mains-frequency AC, motor-drive currents, inverter output currents, and low-frequency switching. It is not intended for high-frequency SMPS gate-drive sensing.
CT07 uses a 1:1000 turns ratio. The secondary current is 1/1000 of the primary current, and designers add a burden resistor to convert that current into a voltage. The burden resistor must be selected to avoid core saturation and to keep the output within the desired sensing range.
No. CT07, like all standard current transformers, requires a changing current to operate. It can measure AC or pulsed DC but cannot sense steady DC because there is no alternating magnetic flux.
CT07 is an encapsulated through-hole transformer with a high dielectric withstand rating of 3750 VAC between primary and secondary. It uses UL 94V-0 materials and supports industrial isolation requirements when installed with proper PCB layout and conductor spacing.
CT07 is optimized for low-frequency or pulsed current measurement and has a relatively low self-resonant frequency, which limits high-frequency operation. Also, because the primary is a user-supplied conductor, its ampacity and thermal performance must be evaluated in the system design.
Choose the burden resistor based on expected current and the 1:1000 turns ratio. The resistor must keep the secondary voltage within the transformer’s volt-microsecond rating and avoid overloading the secondary winding. Following the recommended calculation guidelines prevents saturation and distortion.
Yes. CT07 provides galvanic isolation between the sensed conductor and the measurement circuitry, making it suitable for inverter outputs, battery systems, UPS equipment, and other high-power isolated domains.
CT07 adds virtually no insertion loss, avoids heat dissipation in the sensing element, and offers inherent isolation. However, unlike a shunt, it cannot sense steady DC and requires proper burden resistor selection.
CT07 is most effective in high-current, low-frequency environments such as motor-drive phases, inverter output monitoring, UPS and backup systems, energy-storage equipment, and industrial AC loads where isolation, durability, and low insertion loss are important.