-
Operating Temp. Range: The combination of ambient temperature and temperature rise.
-
Drive Inductance: Tested at 100kHz, 0.1 VRMS.
-
SRF: Values are for reference only.
-
Flammability Standard: Meets UL 94V-0.
-
ET Product: The maximum ET is based upon a flux density of 2800 Gauss at 25°C. Derate the E-T product rating by 20% for operation at 100°C.
ET = EP/2f
Where as, EP = Primary Voltage (V) f = Frequency (Hz) -
Suitable for bipolar applications only.
-
PACKAGING
-
Reel Diameter: 13’’
-
Reel Width: 24 mm
-
Pieces/Reel: 500
-
-
Compliance & Solutions:



-
Specifications subject to change without prior notice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does the GT07 Series offer multiple secondary windings, and how are they typically used?
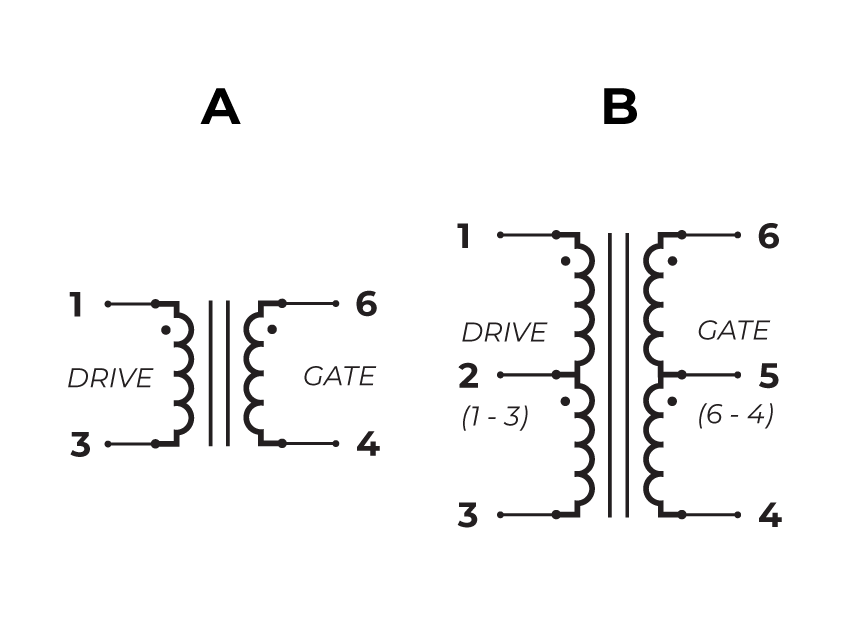
GT07 includes variants with two isolated secondary windings, allowing separate turn-off and turn-on drive paths or providing independent gate signals in half-bridge topologies. This flexibility lets designers tailor gate-drive voltage profiles or apply asymmetric gate strength for improved switching control.
How does the GT07’s magnetizing inductance affect low-duty-cycle operation?
Magnetizing inductance values in GT07 span a wide range (from tens of microhenries to several millihenries depending on the variant). At low duty cycles, insufficient inductance can cause pulse-width distortion because more of the driver’s energy is spent magnetizing the core instead of transferring the pulse. Choosing a variant with adequate inductance ensures accurate gate voltage even at very narrow pulses.
What creepage, clearance, and isolation ratings does GT07 provide and what do they mean for layout?
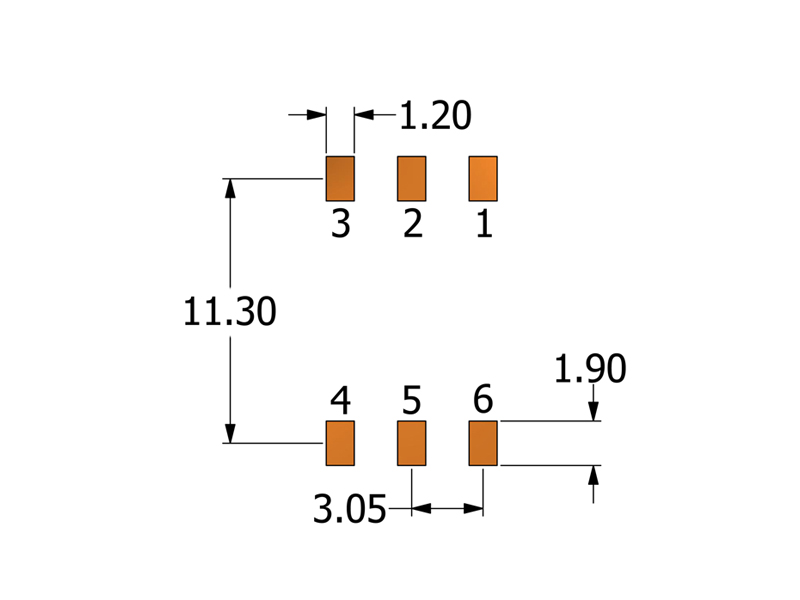
GT07 gate-drive transformers provide approximately 9.2 mm creepage and 8.0 mm clearance between primary and secondary, with a Hi-Pot isolation rating of 6250 VAC. On the PCB, the layout should preserve these distances between isolated nets and avoid copper or components encroaching into that gap, so the assembled design maintains the same isolation capability as the transformer itself.
How should designers interpret the variation in leakage inductance across GT07 models?
Leakage inductance in GT07 varies by winding configuration and wire arrangement. Lower-leakage parts suit fast-switching MOSFETs and SiC devices, while higher leakage can intentionally limit di/dt for quieter switching. Designers can select a variant that aligns with the desired trade-off between speed and EMI.
What determines whether a GT07 variant is appropriate for long-duration drive pulses?
The Volt-microsecond (V-µs) rating defines how long a core can support a given voltage without saturating. Variants with larger ET ratings tolerate longer on-times or lower switching frequencies. If a design uses prolonged turn-on pulses or lower-frequency modulation, a higher ET-rated GT07 transformer should be chosen.
Why does the GT07 provide different DCR values for primary and secondary windings?
DCR variations reflect differences in winding thickness and number of turns. Primary windings often have lower DCR to reduce driver loading, while secondary windings may have higher DCR due to additional turns. These differences affect losses, rise times, and thermal behavior — selecting a proper variant ensures balanced performance.
How does the GT07’s parasitic capacitance influence gate-drive noise immunity?
GT07’s shielded coil structure reduces inter-winding capacitance compared to open-frame designs. Lower parasitic capacitance reduces the amount of common-mode noise coupled into the gate loop, which is critical in high-speed SiC and GaN designs where dv/dt can exceed tens of kV/µs.
What factors make certain GT07 variants more suitable for bidirectional gate-drive schemes?
Variants with symmetrical secondary windings support push-pull gate-drive circuits, allowing strong turn-on and turn-off currents. Because turn-off strength is critical in high-speed devices, symmetric windings help ensure predictable negative gate drive and prevent unintended conduction.
How does temperature affect GT07 core reset requirements?
Core permeability decreases at elevated temperatures, which slightly increases the minimum reset voltage required between pulses. Designers must ensure that thermal rise does not reduce core reset margin in sustained high-frequency operation.
Why is GT07 preferred over toroidal transformers in compact gate-drive modules?
Unlike toroidal cores, GT07’s bobbinized construction provides consistent winding spacing, predictable parasitics, and controlled creepage paths. This makes GT07 easier to integrate into compact driver modules where consistent isolation and repeatable high-frequency performance are required.